The industrial revolution in Pabna is historically significant, particularly in the context of small-scale industries, traditional crafts, and its eventual shift toward a more industrialized economy. Here is an overview of the industrial evolution in Pabna:
1. Pre-Colonial and Colonial Period:Traditional Industries: Pabna has a rich history of traditional industries, especially handloom weaving, which played a central role in its economy. The district was renowned for producing high-quality textiles like muslin and silk.Colonial Influence: During the British colonial period, local industries faced challenges due to competition from imported machine-made goods. Despite this, Pabna’s textile industry survived, supported by skilled artisans and local demand.
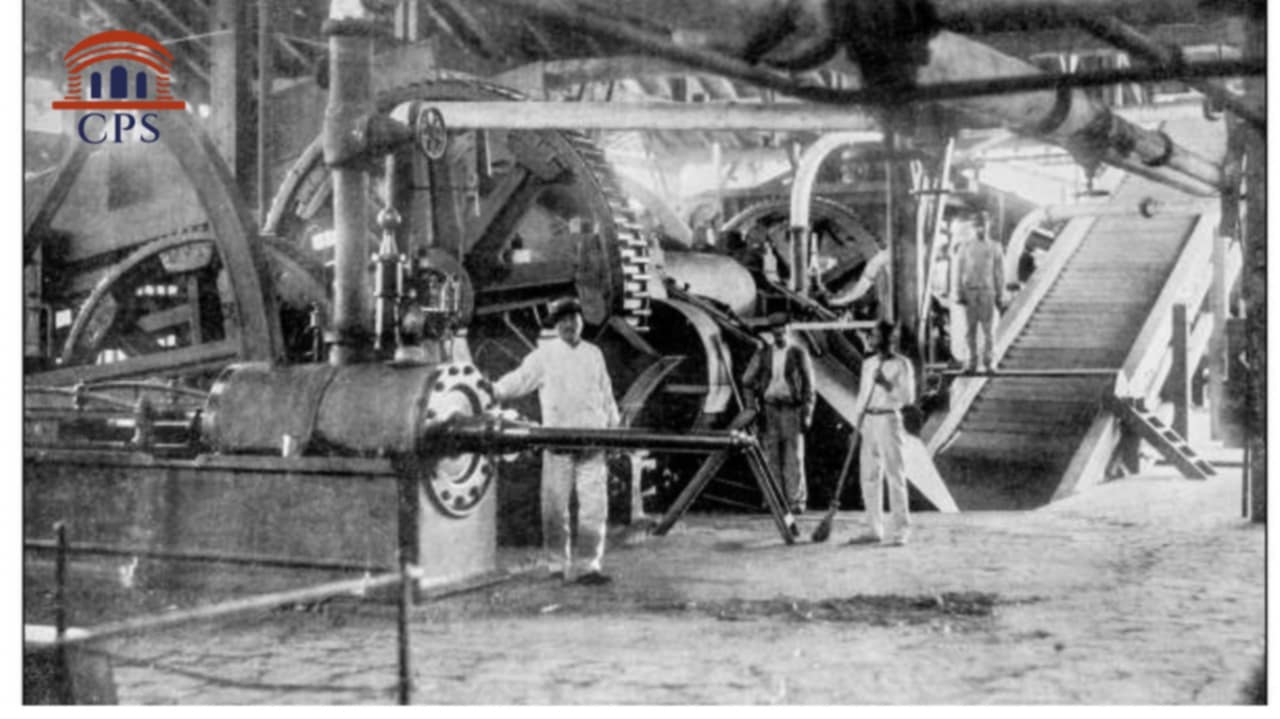
2. Rise of Small-Scale Industries (19th–20th Century):Handloom Industry: Handloom weaving, particularly in Ishwardi and its surroundings, remained the backbone of the district’s economy. The sector employed thousands and contributed significantly to the regional economy.Jute Industry: With the rise of jute cultivation in Bengal, Pabna also became a center for jute-related industries, producing sacks, ropes, and other products.Rice Mills: As agriculture thrived, rice mills emerged as a major industrial activity, catering to both local and national markets.
3. Post-Independence Period (1971–Present):Diversification: After Bangladesh’s independence, the industrial landscape of Pabna began to diversify.Pharmaceutical Industry: Pabna became a hub for the pharmaceutical industry, with prominent companies like Square Pharmaceuticals originating here.Textile Revival: The district saw the revival of textile industries with the establishment of power looms and garment factories.Modern Agriculture Industries: Agro-based industries such as cold storage, food processing, and fertilizer production became prominent.Infrastructure Development: The development of highways, railway connectivity, and the Ishwardi Export Processing Zone (EPZ) has attracted investment in light engineering, electronics, and manufacturing industries.
4. Current Trends:Export-Oriented Industries: Pabna has seen growth in export-oriented sectors, particularly pharmaceuticals, textiles, and agro-based products.Energy and Infrastructure: Ishwardi has become an energy hub with the installation of power plants, boosting industrial growth.EPZ and SEZ: The Ishwardi EPZ has brought foreign and domestic investments, leading to job creation and industrial diversification.Pabna’s industrial revolution reflects a blend of its traditional craft heritage and modern industrial development, making it a key contributor to Bangladesh’s economy.
Edited by: Ananyo Haider, European University of Bangladesh.